BrainSigns expertise is well known worldwide thanks to the many scientific articles published on the most respected international scientific journals.
Technologies involved in our studies are:

Electroencephalography (EEG) is performed with the electroencephalograph, a non-invasive technology, that records the brain signals through the electrodes placed over the scalp thus suitable also for no-laboratory settings. It consists of a measurement method to detect the electrical activity of the brain.

Eye tracking is performed through the eye tracker technology.
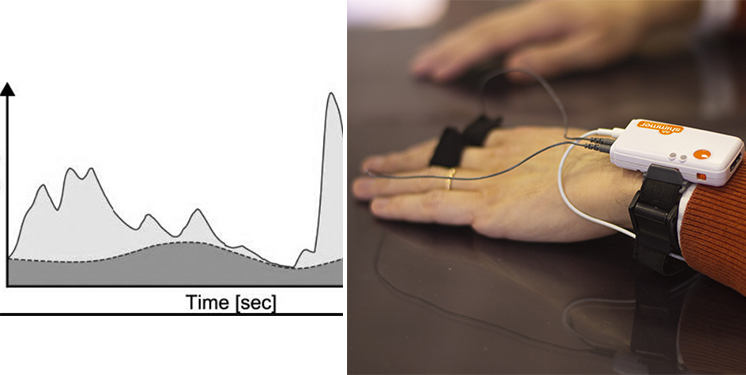
The Galvanic Skin Response (GSR), also known as Electrodermal Activity (EDA) and Skin Conductance (SC), is recorded with a technology which relies on two electrodes, generally placed at the second and third finger of one hand, to capture the continuous variations in terms of electrical characteristics of the skin, i.e. the conductance, caused by the variation of the human body sweating. The variation of a low-voltage applied current between the two electrodes is used as measure of the GSR.
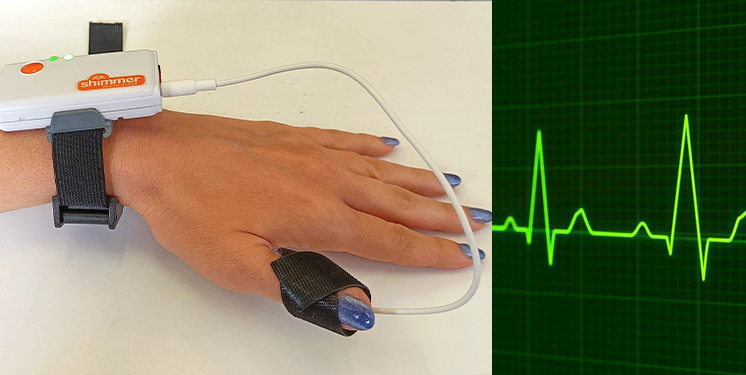
Photoplethysmography (PPG) is performed with a non-invasive technology, an infrared optical sensor, that employs a light source and a photodetector at the surface of skin. It consists of an optical measurement method to detect the volumetric changes in blood circulation.

The Implicit Association Test (IAT) is a tool that has been developed to study the strength of associative links between concepts presented in memory. The IAT is based on the idea that it should be easier and quicker to associate a concept with an attribute when these are strongly correlated in memory than when concepts are weakly associated.

Virtual reality is the term used to indicate a simulated reality, built on a computer, where the user can freely move and interact with the environment. BrainSigns uses it to create immersive scenarios and to study the effect on cognitive and emotional states in different conditions.